It’s interesting to visualize functions of a complex variable, even very simple functions like f(z) = 1/z. The previous post looked at what happens to triangles under the reciprocal map w = 1/z. This post will look at the same map applied to a polar grid, then look at the effect a shift has, replacing 1/z with 1/(z − c).
The function 1/z is a Möbius transformation, and so it maps lines and circles to lines and circles. And in the case of a polar grid, lines go to lines and circles go to circles. The overall grid is unchanged, even though circles swap places with other circles, and lines swap places with other lines. To see this, note that
1/reiθ = (1/r)e−iθ
This means that the function 1/z maps a circle of radius r to a circle of radius 1/r, and it maps a line of slope m to a line of slope −1/m.
Things get more interesting when we shift the reciprocal function to w = 1/(z − c). Now lines will map to circles, unless the line passes through c. Circles will still map to circles, unless the circle passes through c, but we won’t have circles swapping places because the function 1/(z − c) is not its own inverse, unlike 1/z. Here’s a plot with c = 0.1.
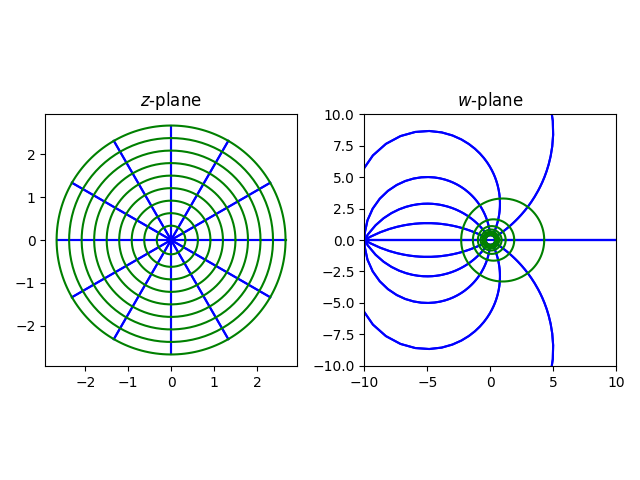
Note that circles map to circles, but the center of a circle does not necessarily map to the center of the image circle. So the green circles in the z-plane map to green circles in the w-plane, but the circles in the z-plane are concentric while their images in the w-plane are not.
The blue lines in the z-plane become blue circles in the w-plane, though some of the circles are too large to fit in the frame of the plot.
As we discussed in the previous post, Möbius transformations are easier to discuss if you adjoint a point at infinity to the complex plane. The radial lines in the z-plane all meet at ∞, and so their images in the w-plane all meet at 1/(∞ – c) = 0.
One final thing to note is that however small ε > 0 is, the images of the grid lines are very different under 1/(z − ε) compared to 1/z. Individual z‘s that start out close together are mapped to w‘s that are close together, but the images of the system of lines and circles is qualitatively different for ε > 0 versus ε = 0.
Related posts
The post Shifted reciprocal first appeared on John D. Cook.